milvus pdf 多模型嵌入实战
一、环境准备
需要提取安装好milvus的环境,推荐使用独立部署的版本,性能相对来说会更好一点。
milvus数据库一般在19530这个端口上
二、模型准备
嵌入模型可以通过魔塔社区去下载,本文选择了3个不同的嵌入模型
python
models = {
"MiniLM": "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
"Jina": "jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-zh",
"GTE": "iic/nlp_gte_sentence-embedding_chinese-base"
}可以直接利用第三方包进行下载
python
from modelscope import snapshot_download
def download(model_name: str = "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
local_dir: str ="./"
):
"""
使用魔塔社区下载
"""
logging.info(f"检测到保存的文件夹{local_dir}")
#判断文件夹是否存在
folder_path=Path(local_dir) / model_name
if folder_path.exists():
logging.info(f"模型已经存在,路径为 {local_dir}")
else:
model_dir = snapshot_download(model_name,local_dir=folder_path)
logging.info(f"模型下载成功,路径为 {local_dir}")
models = {
"MiniLM": "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2",
"Jina": "jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-zh",
"GTE": "iic/nlp_gte_sentence-embedding_chinese-base"
}
for _,value in models.items():
download(model_name=value,local_dir=Path(__file__).parent.absolute())三、处理pdf
对pdf文档进行读取后,完成后续的chunk相关的操作
python
# # 2.读pdf
pdf_path="./Datawhale社区介绍.pdf"
loader = PyPDFLoader(pdf_path)
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=200,
length_function=len,
separators=["\n\n", "\n", " ", ""]
)
# 分割文档
doc_chunks = []
for doc in documents:
chunks = text_splitter.split_text(doc.page_content)
for chunk in chunks:
doc_chunks.append({
'text': chunk,
'source': pdf_path,
'page': doc.metadata.get('page', 0)
})
texts = [doc["text"] for doc in doc_chunks]
metas = [(doc["source"], doc["page"]) for doc in doc_chunks]四、多个模型嵌入
在语义召回中,有时单个语义没有办法很准确的召回用户查询的信息,同时不同的嵌入模型的维度大小不同,对于同一个问题,不同的维度在相似性匹配时速度不同,对语义噪音的容忍度不同,因此可以对同一个pdf文本构建多个不同的模型嵌入,根据实际的性能以及准确度的要求进行单模型或者多模型的选择
python
from pymilvus import connections, utility, Collection, FieldSchema, CollectionSchema, DataType
connections.connect("default", host="localhost", port="19530")
for name, model_path in models.items():
print(f"🔍 正在加载模型 {name}...")
model = SentenceTransformer(model_path)
print(f"🔄 正在进行嵌入:{name}")
vectors = model.encode(texts, show_progress_bar=True, normalize_embeddings=True)
dim = vectors.shape[1]
collection_name = f"rag_{name.lower()}"
# 如果存在旧 collection,先删掉重建
if utility.has_collection(collection_name):
Collection(collection_name).drop()
print(f"📦 创建 Milvus collection:{collection_name}")
# 创建 schema
fields = [
FieldSchema(name="id", dtype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True, auto_id=True),
FieldSchema(name="embedding", dtype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=dim),
FieldSchema(name="text", dtype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=10000),
FieldSchema(name="source", dtype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=2000),
FieldSchema(name="page", dtype=DataType.INT64)
]
schema = CollectionSchema(fields=fields, description=f"{name} embedding collection")
collection = Collection(name=collection_name, schema=schema)
collection.create_index("embedding", {"index_type": "IVF_FLAT",
"metric_type": "COSINE",
"params": {"nlist": 128}}
)
collection.load()
# 插入数据
print(f"📥 写入 {len(texts)} 条数据到 Milvus({collection_name})")
collection.insert(
data = [
vectors.tolist(),
texts,
[s for s, _ in metas],
[p for _, p in metas],
],
columns=["embedding", "text", "source", "page"]
)
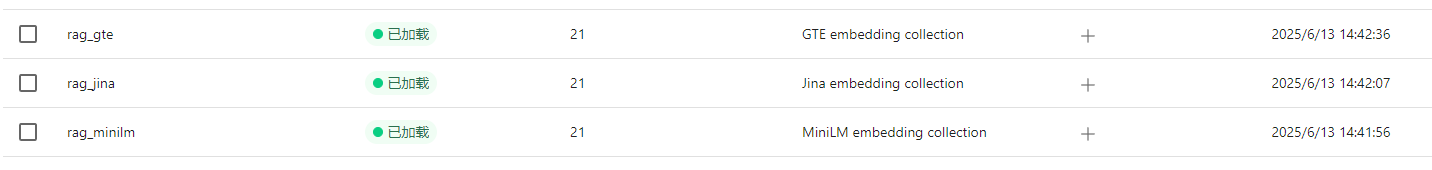
print(f"✅ [{name}] 已完成写入!")可以看到milvus在default库中建了3个表
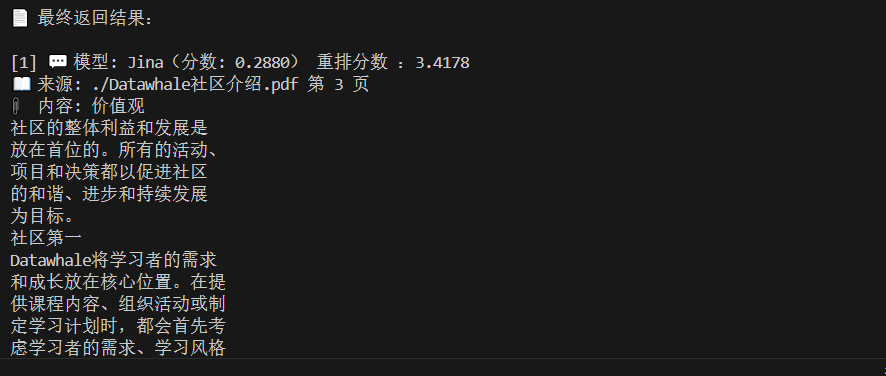
五、模型召回与重排
先将使用向量库的search搜索,找到粗召回的相关资料,然后使用reranker对内容进行二次排序,提供精确度。
重排是使用专用的重排模型对召回的内容进行比较,相对来说准确度会更高
python
from FlagEmbedding import FlagReranker
reranker = FlagReranker('./BAAI/bge-reranker-base', use_fp16=True) # use_fp16=False 可在 CPU 上运行
query = "量子计算的应用场景"
documents = [
"量子计算机的工作原理",
"人工智能发展简史",
"量子加密技术的最新进展"
]
# 组成句对
pairs = [[query, doc] for doc in documents]
# 计算得分
scores = reranker.compute_score(pairs)
# 输出排序结果
results = sorted(zip(documents, scores), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for doc, score in results:
print(f"得分: {score:.4f} | 文档: {doc}")
###########结果##############
#得分: 1.6082 | 文档: 量子计算机的工作原理
#得分: -1.7742 | 文档: 量子加密技术的最新进展
#得分: -3.8244 | 文档: 人工智能发展简史使用collection.search进行数据搜索,使用reranker进行二次的准确度计算。
python
def search_question(reranker,query: str, top_k: int = 5):
all_results = []
for name, collection in collections.items():
print(f"🔎 使用模型 [{name}] 查询...")
# 生成查询 embedding
embedding = models[name].encode(query, normalize_embeddings=True).tolist()
# 向量检索
res = collection.search(
data=[embedding],
anns_field="embedding",
param={"metric_type": "COSINE", "params": {"nprobe": 10}},
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["text", "source", "page"]
)
for hit in res[0]:
all_results.append({
"model": name,
"text": hit.entity.get("text"),
"source": hit.entity.get("source"),
"page": hit.entity.get("page"),
"score": hit.distance
})
# 去重(以文本为准)
unique = {}
for r in all_results:
if r["text"] not in unique or r["score"] < unique[r["text"]]["score"]:
unique[r["text"]] = r
deduped_results = list(unique.values())
# === 重排开始 ===
pairs = [[query, r["text"]] for r in deduped_results]
rerank_scores = reranker.compute_score(pairs)
for i in range(len(deduped_results)):
deduped_results[i]["rerank_score"] = rerank_scores[i]
# 排序
final_results = sorted(deduped_results, key=lambda x: x["rerank_score"], reverse=True)
return final_results[:top_k]看一下最终的召回结果